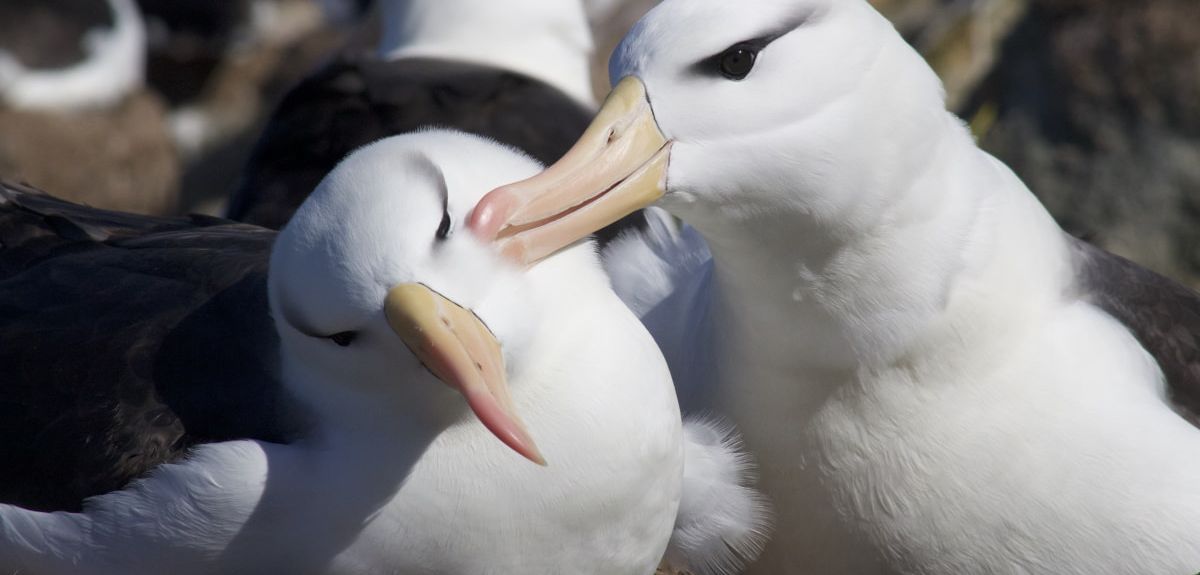

Credit: Tim Guilford
Oxford researchers discover unexpected deep diving in albatross
Data collected by the team revealed that 50% of the birds studied were capable of diving over twice the depth previously thought, with implications for conservation efforts of this endangered species.
In a recent study published in Current Biology, a collaboration between researchers from Oxford University, University of Lisbon and the British Geological Survey found that black-browed albatross dive deeper than previously realised.
Mollymawks (small to medium-sized albatross like the black-browed albatross) are known to shallow dive, reaching a maximum diving depth of 6m–9m. Data collected by the team revealed that 50% of the birds dived deeper than 10m and that dives could be up to 19m deep – over twice the depth previously thought.
GPS devices, depth recorders and accelerometers documented the journeys of the New Island population in the Falklands commuting to the South American coast and diving at unexpected depths to pursue prey.
Dr Oliver Padget, Junior Research Fellow, Department of Zoology at the University of Oxford said:
‘A better understanding of the unobserved behaviour of the albatross and other endangered seabirds is essential to conservation efforts.
‘That black-browed albatross are physically capable of such deep dives will now need to be considered when thinking about the effectiveness of mitigation strategies that rely on the species being restricted to the surface.’
Diving activities recorded amongst the population took place during the day, suggesting that the albatross rely on their vision to pursue shoaling prey on deeper dives.
‘We found that deep diving was restricted to daylight hours, and so one potential mitigation could be for pelagic long lines to be set at night when albatross might be less likely, or able, to chase baits and become caught.’ Dr Padget continued.
The albatross, the harbourer of mariners’ souls, is facing a conservation crisis. Plummeting populations over recent decades have left albatross in the number of the world’s most imperilled species. 15 of 22 species in the albatross family are at threat of extinction.
A major factor in the decline has been modern commercial fishing methods. Seabirds are incidentally caught by vessels targeting large ocean-going fish, such as tuna, using pelagic longlines.
Generally observed as surface feeders, with a powerful sense of smell and shallow diving ability, hungry albatross are at particular risk when lines are set, and the baited hooks are still close to the surface.
Bycatch mitigation measures can reduce the potential dangers by limiting the availability of hooks to birds as lines sink from the surface (using weights to sink lines faster or Hookpods that cover the barb).
These techniques focus on the danger from lines near the surface because albatross are not [usually] documented diving at depths where the hooks are deployed for the target catch.
Tim Guilford, Professor of Animal Behaviour, Department of Zoology at the University of Oxford said:
‘Diving in this population could be the result of previously unseen behavioural flexibility, and have important consequences for how we think about the risks to threatened species, and for how they might respond to change.’
Read the published findings on Current Biology.
 New study on Amazonia's fire crises urges action ahead of the next burning season
New study on Amazonia's fire crises urges action ahead of the next burning season
 New heart disease calculator could save lives by identifying high-risk patients missed by current tools
New heart disease calculator could save lives by identifying high-risk patients missed by current tools
 Modern Slavery and Human Rights Policy and Evidence Centre moves to Oxford University after receiving continuation funding
Modern Slavery and Human Rights Policy and Evidence Centre moves to Oxford University after receiving continuation funding
 Study shows that island bats are valuable allies for farmers
Study shows that island bats are valuable allies for farmers
 Study reveals how humanity could unite to address global challenges
Study reveals how humanity could unite to address global challenges